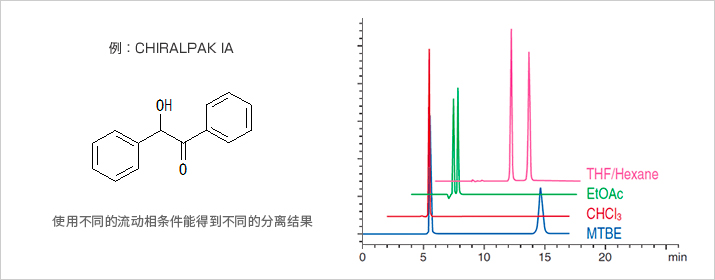
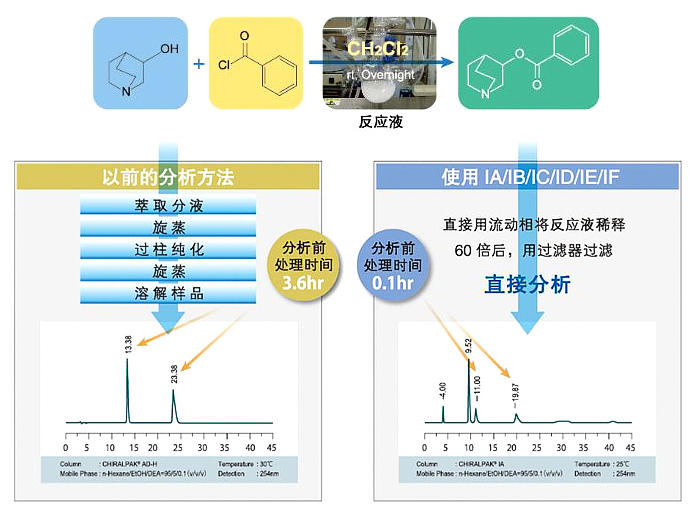
相关文献
● Profiling of branched chain and straight chain saturated fatty acids by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry, X. Fu, N. Hafza, F. Götz, M. Lämmerhofer, J. Chromatogr. A, 1703, issue #16, (2023)
● The Chiral Separation of the (+) and (-) Enantiomers of Cannabidiol, W. Umstead, Cannabis Science and Technology, 5, issue #5, (2022), 30-34
● The separation of several organophosphate pesticides on immobilized polysaccharide chiral stationary phases, W. Champion Jr, W. Watts Jr, W. Umstead, Chirality, 34, issue #8, (2022), 1078-1093
● ON/OFF receptor-like enantioseparation of planar chiral 1,2-ferrocenes on an amylose-based chiral stationary phase: The role played by 2-propanol, C. Cantatore, M. Korb, H. Lang, R. Cirilli, Analytica Chimica Acta, 1211, (2022)
● Characteristic and complementary chiral recognition ability of four recently developed immobilized chiral stationary phases based on amylose and cellulose phenyl carbamates and benzoates, T. Onishi, T. Ueda, K. Yoshida, K. Uosaki, H. Ando, R. Hamasaki, A. Ohnishi, Chiralty, (2022), 1-16
● Investigation of retention behavior of natural cannabinoids on differently substituted polysaccharide-based chiral stationary phases under reversed-phase liquid chromatographic conditions, C. De Luca, A. Buratti, W. Umstead, P. Franco, A. Cavazzini, S. Felletti, M. Catani, J. Chromatogr. A, 1672, (2022)
● Single-run chemo- and enantio-selective high-performance liquid chromatography separation of tramadol and its principal metabolite, O-desmethyltramadol, using a chlorinated immobilized amylose-based chiral stationary phase under multimodal elution conditions, C. Cantatore, G. La Regina, R. Ferretti, R. Silvestri, R. Cirilli, Sep Sci Plus, (2022), 1-6
● Towards enantioselective ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry-based metabolomics of branched-chain fatty acids and anteiso-fatty acids under reversed-phase conditions using sub-2-μm amylose- and cellulose-derived chiral stationary phases, C. Geibel, L. Zhang, K. Serafimov, H. Gross, M. Lämmerhofer, Chiralty, (2022), 1-14
● DoE Optimization Empowers the Automated Preparation of Enantiomerically Pure [18F]Talazoparib and its In Vivo Evaluation as a PARP Radiotracer, G. D. Bowden, S. Stotz, J. Kinzler, C. Geibel, M. Lämmerhofer, B. J. Pichler, A. Maurer, J. Med. Chem., 64, issue #21, (2021), 15690–15701
● The Separation of Cannabinoids on Sub-2 μm Immobilized Polysaccharide Chiral Stationary Phases, T. Onishi, W. J. Umstead, Pharmaceuticals, 14, issue #12, (2021)
● The Separation of Several Minor Cannabinoids via Chiral HPLC, W. J. Umstead, Cannabis Science and Technology, 4, issue #6, (2021), 44-51
● Enantiomeric methadone quantitation on real post-mortem dried matrix spots samples: Comparison of liquid chromatography and supercritical fluid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry, F. Mueller, G.L. Losacco, R. Nicoli, D. Guillarme, A. Thomas, E. Grata, J. Chromatogr B., (2021)
● Solvent versatility of immobilized 3,5-dimethylphenylcarbamate of amylose in enantiomeric separations by HPLC, T. Zhang, C. Kientzy, P. Franco, A. Ohnishi, Y. Kagamihara, H. Kurosawa, J. Chromatogr. A, 1075 (2005) 65-75
● Cellulose 3,5-dimethylphenylcarbamate immobilized on silica: A new chiral stationary phase for the analysis of enantiomers, T. Zhang, D. Nguyen, P. Franco, T. Murakami, A. Ohnishi, H. Kurosawa, Anal. Chim. Acta, 557 (2006) 221-228
● Cellulose tris(3,5-dichlorophenylcarbamate) immobilised on silica: A novel chiral stationary phase for resolution of enantiomers, T. Zhang, D. Nguyen, P. Franco, Y. Isobe, T. Michishita, T. Murakami, J. Pharm. Biochem. Anal., 46 (2008) 882-891
● Common approaches for efficient method development with immobilised polysaccharide-derived chiral stationary phases, P. Franco, T. Zhang, J. Chromatogr. B, 875 (2008) 48
● Enantiomer resolution screening strategy using multiple immobilised polysaccharide-based chiral stationary phases, T. Zhang, D. Nguyen, P. Franco, J. Chromatogr. A, 1191 (2008) 214-222
● Complementary enantiorecognition patterns and specific method optimization aspects on immobilized polysaccharide-derived chiral stationary phases, T. Zhang, P. Franco, D. Nguyen. R. Hamasaki, S. Miyamoto, A. Ohnishi. T. Murakamo, J. Chromatogr. A, 1269 (2012) 178–188